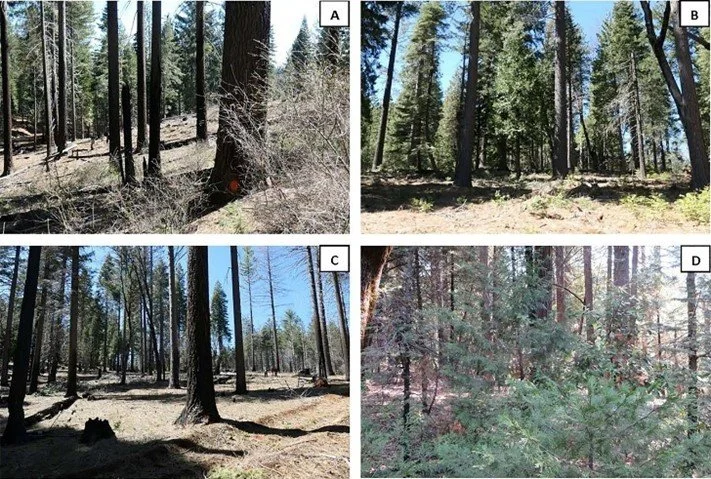
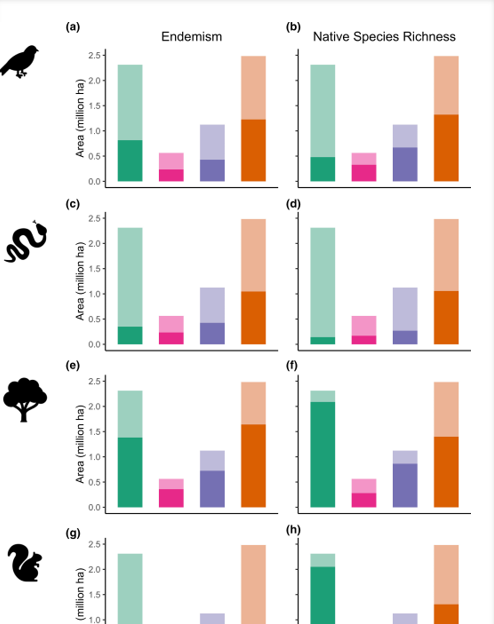
Thinning + burning treatments effectively reduce fire severity
/Although fuels treatments are generally shown to be effective at reducing fire severity, there is widespread interest in monitoring that efficacy as the climate continues to warm and the incidence of extreme fire weather increases. This paper compared basal area mortality across adjacent treated and untreated sites in the 2021 Dixie Fire of California’s Sierra Nevada.
View Full Article (Open Access)
Read More